The Asia Zero Emission Community (AZEC) Concept: Promoting Decarbonization in Asia
Efforts Being Advanced by Japanese Companies
(Provisional translation)
(English ver.) 2024-07-19

In 2022, Japan put forward the concept of the Asia Zero Emission Community (AZEC) as a platform aiming to achieve decarbonization while supporting fast growing economies in Asia. In December 2023, the first AZEC Leaders Meeting by partner countries was held, and the AZEC Leaders’ Joint Statement was adopted. It has been confirmed that more than 350 cooperation projects are underway among governments, companies and financial institutions in Japan and other partner countries with memorandums of understanding (MOUs) signed for some projects. This article sheds light on some examples of such projects.
More than 350 cooperation projects underway between Japan and other Asian countries
The Asia Zero Emission Community (AZEC) concept was proposed by Japan aiming for an energy transition from fossil fuels towards decarbonization while supporting economic growth in the respective countries of the Asian region. At the Leaders Meeting held in December 2023, the AZEC principles towards decarbonization were confirmed, and various agreements were reached on technical cooperation and policy development support. The AZEC Leaders’ Joint Statement was adopted as an outcome document.
There are more than 350 cooperation projects underway among governments, companies and financial institutions in Japan and other partner countries. These include 68 projects with MOUs executed as announced at the Leaders Meeting.
Policy coordination and project cooperation are being advanced in tandem in these projects.
These projects cover a wind range of cooperation in the development and demonstration of decarbonization technologies such as renewable energy (solar, wind, and geothermal power), energy efficiency improvement, hydrogen, ammonia, biomass, and CCS/CCUS, as well as the promotion of transition finance. The Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry compiled efforts being made in these projects and published the AZEC Progress Report 2023 and the List of MOUs towards the AZEC Leaders Meeting.
Cooperation projects taking advantage of Japan’s advanced technologies
The following two examples represent cooperation projects between Japan and AZEC partner countries.
Example 1: Building a plant to produce green hydrogen in Malaysia
Asahi Kasei Corporation, JGC Holdings Corporation (JGC) and Gentari Sdn Bhd (Gentari), a subsidiary of PETRONAS (Malaysia’s national oil and gas company), signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) for production of up to 8,000 tons per year of green hydrogen using a 60 megawatt (MW)-class alkaline water electrolysis system.

MOU signing ceremony held at Asahi Kasei’s head office
(Source) Press release by Asahi Kasei
This project is being operated as part of the project of the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO). It is expected that green hydrogen production in Malaysia will create markets in Japan and Malaysia as well as in other Southeast Asian countries, leading to the establishment of production infrastructure for green hydrogen towards decarbonization in the region.
Gentari’s Chief Hydrogen Officer commented as follows:
“The project stands as a catalyst for advancing Malaysia’s hydrogen economy towards achieving its green hydrogen target of 200,000 tons per year by 2030, aligning with the National Energy Transition Roadmap and Hydrogen Economy and Technology Roadmap. Beyond this, Gentari is developing hydrogen projects with national and state entities to position Malaysia as the region’s leading hydrogen hub.”
Example 2: Producing sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) from Indonesia’s non-standard coconuts
Indonesia is one of the largest producers of coconuts. A company named Green Power Development Corporation of Japan (GPD) is tackling a project to establish a supply chain for neat SAF.* In this project, the company procures inedible, non-standard coconuts that are too small or have sprouted and conducts oil extraction to produce crude coconut oil (CCO) for export to Japan for the production of neat SAF.
Neat SAF: Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) of 100% purity produced from biomass materials
SAF needs to be produced from feedstocks and technologies certified by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), an organization under the UN. If feedstocks are approved by the ICAO, they will be included in the SAF feedstock Positive List as environmentally sustainable feedstocks. As non-standard coconuts were not utilized to produce fuels, obtaining certification from the ICAO was thought to be unlikely. However, under NEDO’s project titled the Development of Production Technologies for Biojet Fuels, Green Power Development Corporation of Japan (GPD) started its efforts in 2022 towards setting a detailed definition of non-standard coconuts and developing a screening system, and eventually succeeded in having them registered in the ICAO Positive List in March 2023.
Definition of Non-Standard Coconuts
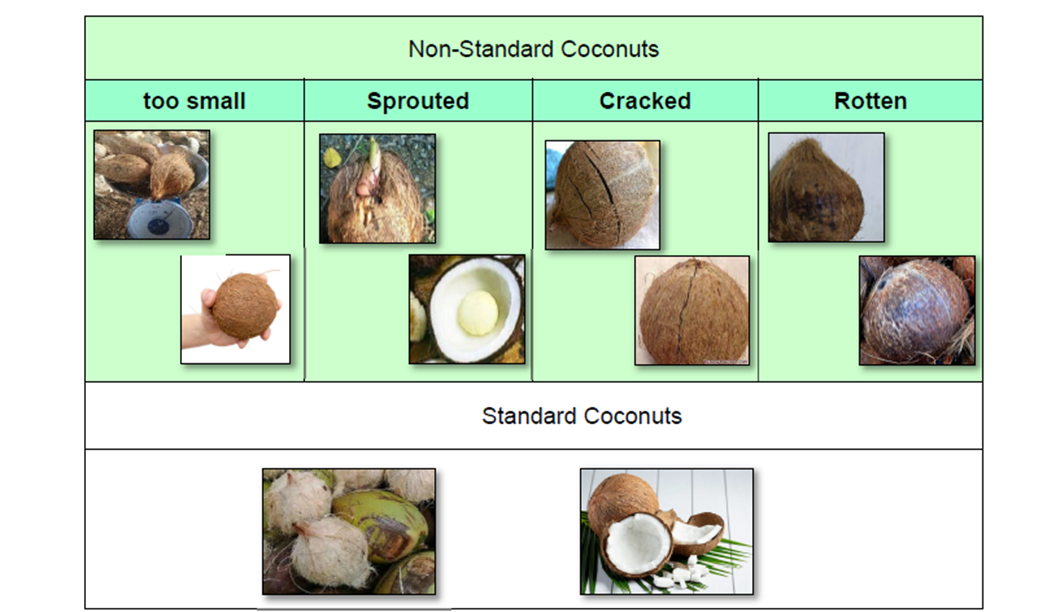
(Source) Green Power Development Corporation of Japan
In 2022, the supply of SAF only accounted for 0.1% of the total jet fuel supply in the world. It is hoped that its production and utilization will increase as rapidly as possible. Some 700 to 100 million tons of coconuts are produced in the world, approximately 30% of which are presumed to be non-standard and could become promising SAF feedstock.
Positive responses to the AZEC concept from countries in Southeast Asia
The AZEC platform is welcomed in countries in Southeast Asia. Some of the comments at the time of the AZEC Leaders Meeting carried in the local newspapers are listed below:
-
 President Joko of Indonesia said that he expected AZEC to be a practical platform for partner countries to join in the emission reduction efforts in the spirit of cooperation. (Kompas, Indonesia)
President Joko of Indonesia said that he expected AZEC to be a practical platform for partner countries to join in the emission reduction efforts in the spirit of cooperation. (Kompas, Indonesia)
-
 Malaysia is certain that AZEC will function as a long-term platform to promote reciprocal cooperation in energy transition particularly in our region. (Borneo Post, Malaysia)
Malaysia is certain that AZEC will function as a long-term platform to promote reciprocal cooperation in energy transition particularly in our region. (Borneo Post, Malaysia)
-
 President Marcos of the Philippines stated that his country, together with other AZEC partner countries, recognized the necessity of accelerating an energy transition that is clean, sustainable, fair, inexpensive, and comprehensive. (Manila Times, the Philippines)
President Marcos of the Philippines stated that his country, together with other AZEC partner countries, recognized the necessity of accelerating an energy transition that is clean, sustainable, fair, inexpensive, and comprehensive. (Manila Times, the Philippines)
High hopes for the AZEC concept have been expressed by AZEC partner countries as seen in the above statements.
Japan, together with other partner countries, will contribute to decarbonization in Asia and sustainable growth in the world through the AZEC platform.
Divisions in Charge
About this article
International Affairs Division, Commissioner’s Secretariat, ANRE
About the Special Contents
Research and Public Relations Office, Commissioner’s Secretariat, ANRE
![]() The original Japanese text of this article; Click here
The original Japanese text of this article; Click here

